When an object is spun around in a circle it is accelerated outward by centrifugal force
When liquid is spun around in a circle, it accelerates outward from the center of the circle due to centrifugal force

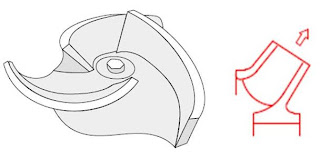
Liquid enters the pump suction (nozzle) and then into the eye (center) of the impeller.
When the impeller rotates, it spins the liquid sitting between the vanes outward and provides centrifugal acceleration.
As liquid leaves the eye of the impeller, a low-pressure area is created causing more liquid to flow toward the inlet. Because the impeller blades are curved, the fluid is pushed in a tangential and radial direction by the centrifugal force.

Conversion of Kinetic Energy to Pressure Energy
Centrifugal force creates the kinetic energy.
The amount of energy given to the liquid is proportional to the velocity at the edge or vane tip of the impeller. The faster the impeller revolves or the bigger the impeller is, the higher will be the velocity of the liquid at the vane tip and the greater the energy imparted to the liquid.